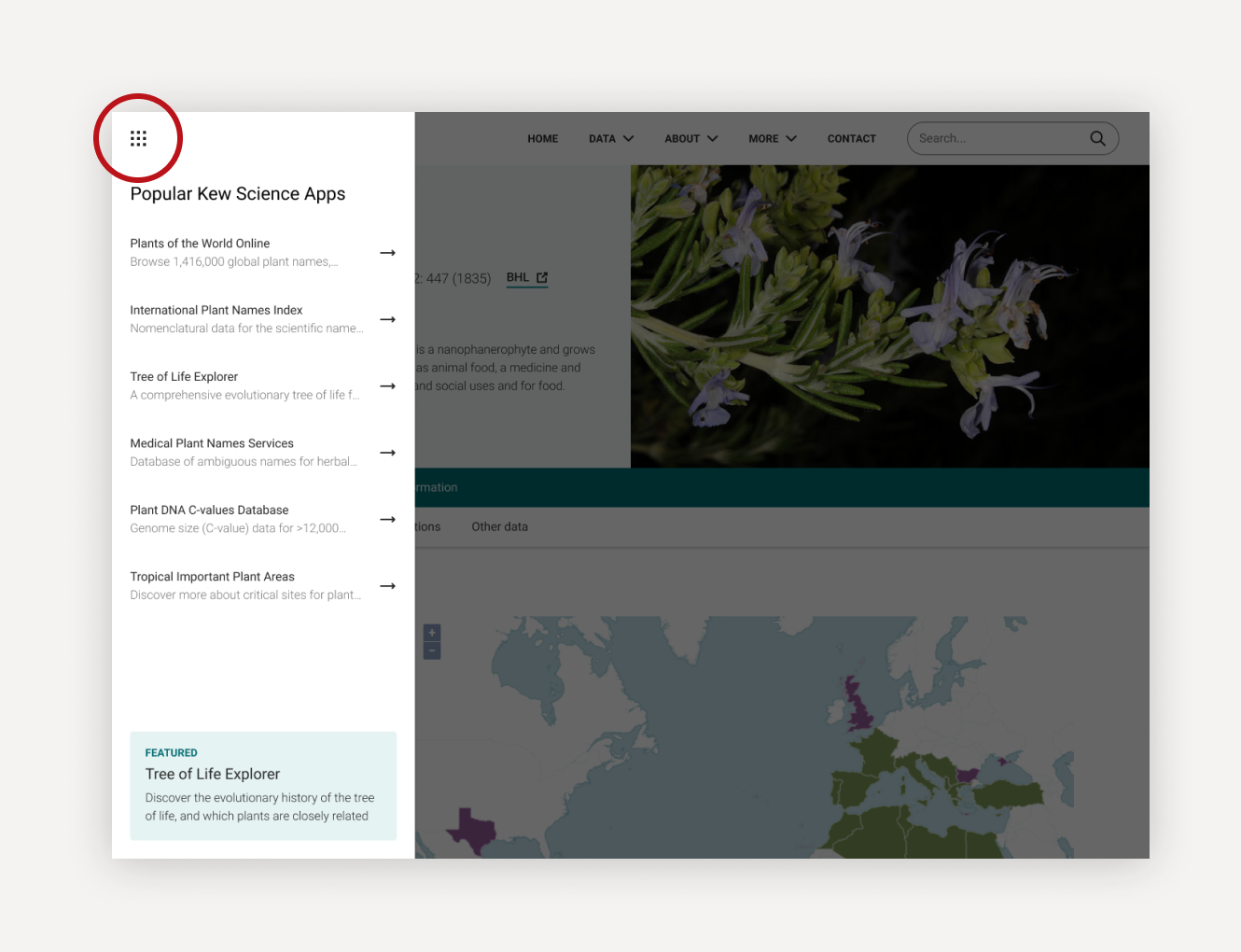
Discover what else Kew Science has to offer
We’re trialling a new ‘app switcher’ feature to help our users move between our science apps. For now we’ve just listed some of our more popular apps, but soon we hope to show more and roll it out across all our science websites.
Let us know what you think via the link at the bottom of the app switcher.