Legumes of the World. Edited by G. Lewis, B. Schrire, B. MacKinder & M. Lock. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. (2005)
-
Note
-
The tribe Desmodieae as treated by Ohashi et al. (1981) comprised 27 genera and c. 540 species in three subtribes, the Bryinae, Desmodiinae and Lespedezinae. Molecular analyses by Bailey et al. (1997) and Doyle et al. (2000) show that Bryinae has affinities elsewhere; Lavin et al. (2001a) place it within the Pterocarpus clade of the Dalbergieae sens. lat. (see page 309). The Bryinae are therefore removed from the Desmodieae here, as are two genera formerly placed in subtribe Lespedezinae; Phylacium Benn. and Neocollettia Hemsl., which are moved to tribe Phaseoleae (see page 393) on morphological, palynological and molecular evidence (Doyle et al., 2000; Kajita et al., 2001). The two remaining subtribes of Desmodieae are recognised in this treatment as three groups, the Lespedeza, Phyllodium and Desmodium groups, based on results of an analysis of the chloroplast gene rbcL (Kajita et al., 2001). The Phyllodium and Desmodium groups correspond to subtribe Desmodiinae, and the Lespedeza group to subtribe Lespedezinae (with Campylotropis now comprising 37 instead of 65 species as in Ohashi et al., 1981).
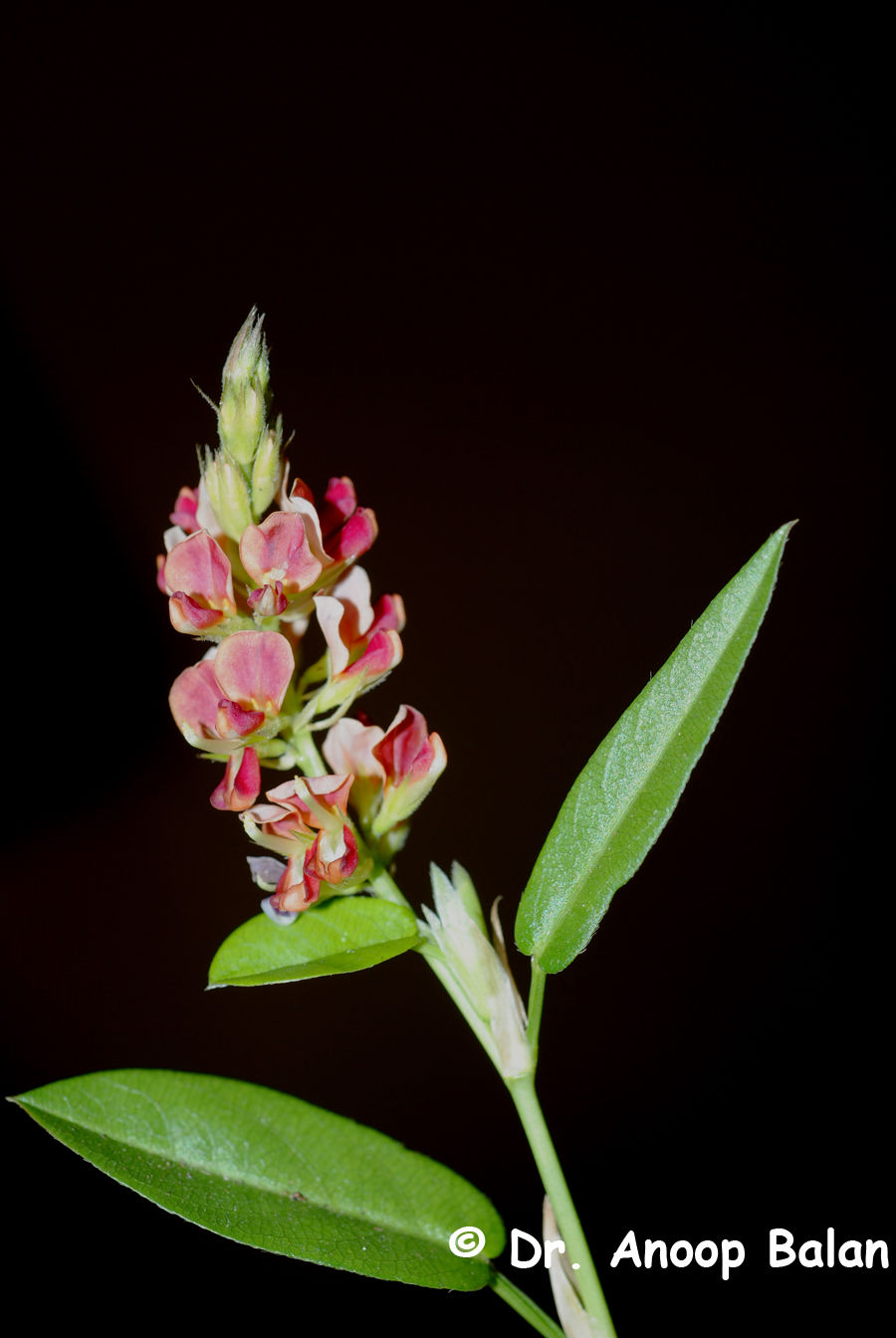
Desmodieae as circumscribed here comprises 30 genera and (524)–527–(530) species (Fig. 48). The tribe occurs in the tropical, subtropical and warm temperate regions of the world, but extends into the cool temperate and sub-boreal regions of E Asia and N America (except W of the Rocky Mountains). At generic level subtribe Desmodiinae is most diverse in tropical S and SE Asia (Dy Phon et al., 1994), while temperate E Asia (Yang & Huang, 1995) and N America (Isely, 1998) are the centres of diversity of subtribe Lespedezinae. The tribe occurs widely from coastal to montane areas, but not at high altitudes. Species are most commonly shrubs or subshrubs, sometimes herbs, rarely trees and are usually erect and 3-foliolate.
The Desmodieae have been considered similar to tribe Phaseoleae (Polhill, 1981a) and were recently shown to be a monophyletic lineage included within Phaseoleae sens. lat. (Fig. 47, page 394), closely related to subtribe Kennediinae (Doyle & Doyle, 1993, Bruneau et al., 1995; Doyle et al., 1997) and possibly sister to Mucuna (Bailey et al., 1997; Doyle et al., 2000; Kajita et al., 2001).
-
Habit
-
Herbs
-
Ecology
-
Seasonally dry tropical woodland, wooded grassland and grassland, often in seasonally wet or open sandy and ruderal areas
-
Distribution
-
Africa (c. 10 spp., c. 5 endemic), India, Indo-China, Malesia, China, E Asia and Japan (c. 20 spp.) and Australia (8 spp., c. 2 endemic); endemic species are mostly in India (15 spp.)