Legumes of the World. Edited by G. Lewis, B. Schrire, B. MacKinder & M. Lock. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. (2005)
-
Note
-
Previous accounts of the Phaseoleae by Baudet (1978) and Lackey (1981) recognised 90 and 84 genera and c. 1540 and 1480 species respectively in the tribe. In an equivalent, i.e. traditionally held view of Phaseoleae, 89 genera and (1554)–1567–(1580) species are treated here (Table 9; Fig. 47). Changes between Baudet (1978) and this treatment are that eleven genera are now in synonymy or have subsequently been placed in Millettieae, two genera have been transferred from Desmodieae and eight new genera have been added. Vigna has traditionally been thought to comprise some 150–200 species, but Vigna sens. strict. may contain fewer than 100.
Recent molecular analyses of the tribe, however, have emphasised both the polyphyletic and paraphyletic nature of Phaseoleae as traditionally circumscribed (Bruneau & Doyle, 1990; Doyle & Doyle, 1993; Delgado Salinas et al., 1993; Bruneau et al., 1995; Doyle et al., 1997, 2000; Kajita et al., 2001; Goel et al., 2001; Lee & Hymowitz, 2001). This has required a radical realignment of elements of the phaseoloids (Table 9; Fig. 47), with at least two major clades being evident: Phaseoleae subtribes Diocleinae and Ophrestiinae which together with tribe Abreae are allied to the core-Millettieae (Fig. 45), and the remaining groups comprising a Phaseoleae sens. lat. clade. The rbcL phylogeny of Kajita et al. (2001) and the ITS analysis of Hu et al. (2002) are equivocal as to which clade subtribe Clitoriinae belongs. Phaseoleae sens. lat. also includes two traditionally independent tribes, the Desmodieae and Psoraleeae. Delimiting a recircumscribed Phaseoleae sens. strict is thus very problematic. A solution may be to recognise a broad tribe Phaseoleae, comprising the subtribes Kennediinae, Cajaninae, Phaseolinae and Glycininae, assorted basally branching genera, and tribes Desmodieae and Psoraleeae (both treated at subtribal level).
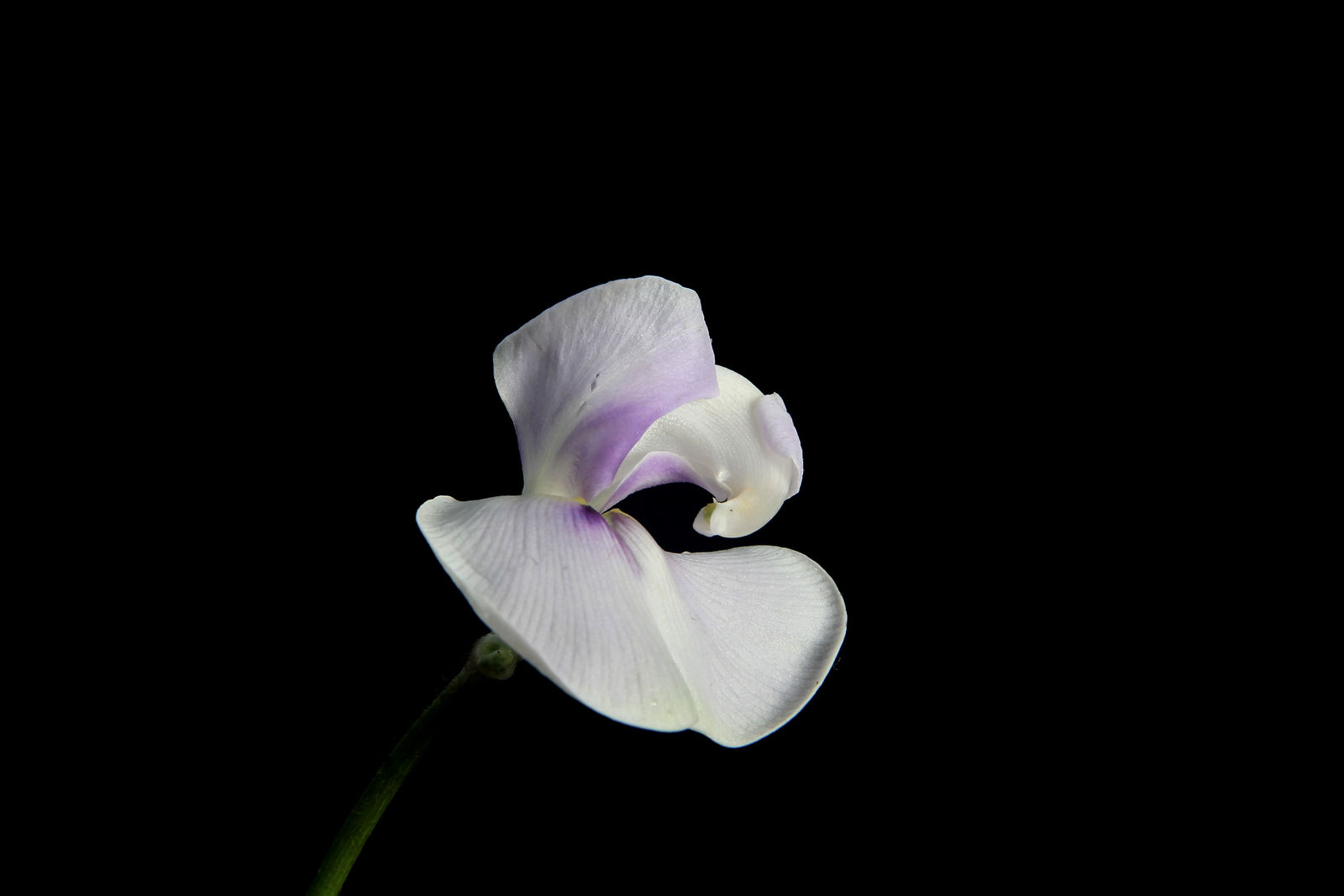
The New World species of Vigna may be significantly reduced with the removal of subgenus Sigmoidotropis (c. 17 spp., including V. caracalla (L.) Verdc., illustrated above) which is polyphyletic with respect to the rest of Vigna (Delgado Salinas et al., 1993)
-
Habit
-
Herbs
-
Ecology
-
Seasonally dry tropical woodland, wooded grassland and grassland, often in well drained sites with low fertility
-
Distribution
-
Palaeotropics and subtropics (c. 80-85 spp., mostly in Africa [c. 55-60 spp.; 4 spp. endemic to Madagascar] and SE Asia [c. 21 spp.]), c. 22 spp. in Neotropics and subtropics (but see taxonomic notes)