Geography and distribution
Alfalfa is thought to have originated in Iran and it has been used as a fodder crop since Roman times.
The largest producer of alfalfa today is North America, followed by Europe, South America and Asia. Alfalfa is grown in many other parts of the world, from China to Spain, Sweden to North Africa. Outside of cultivation alfalfa occurs as a weed throughout Asia, Europe and America.
Description
Overview: Medicago sativa is a perennial herb living for several years. It has erect stems up to 60 cm tall with many branches.
Leaves: The leaflets are 5-20 mm long and dentate (toothed) at the apex and sometimes at the base.
Flowers: The flowers, which are violet to pale lavender, are clustered along an unbranched axis (known as a raceme). The flowers are papilionaceous, typical of species belonging to the subfamily Papilionoideae, and resemble, for example, the pea flower. The calyx, the outer whorl of floral organs, has teeth which are as long as the floral tube (corolla). The corolla is composed of petals fused into a tube which is 6-12 mm long.
Fruit: A curved or loose spiral seed pod containing 10 to 20 seeds which are yellow to brown in colour.
Uses
Alfalfa is one of the most nutritious forage crops available and in addition to its high protein content, is an important source of important vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A and calcium. This multi-purpose forage crop is harvested mainly as hay but can also be processed into silage and meal, or grazed on. Pelleted alfalfa meal is used in mixed feeds for cattle, poultry and other animals.
Alfalfa is sometimes grown as a cover crop to reduce soil erosion and often increases yields of succeeding crops such as potatoes, rice and tomatoes.
The seeds of alfalfa can be sprouted and prepared in salads or sandwiches for human consumption. Care should be taken because when consumed raw, alfalfa seeds and sprouts contain the amino acid canavanine which can have a toxic effect in primates, including humans, and can result in lupus-like symptoms in susceptible individuals. The effects can be reversed by stopping the consumption of alfalfa. In parts of Russia and China tender alfalfa leaves serve as a vegetable.
Alfalfa can be used medicinally to treat a variety of ailments for example, in India and China the plant has been used for centuries to relieve fluid retention and to treat kidney stones.
In folklore, it is believed that alfalfa offers protection and the ashes of burnt alfalfa are scattered around a property to guard against negative influences. In pagan rituals alfalfa is used to protect the home from poverty and hunger.
Other uses include manufacturing paper from alfalfa fibre and extracting a yellow dye from the seeds.
Crop wild relatives of alfalfa
The Millennium Seed Bank and the Global Crop Diversity Trust are engaged in a ten-year project, called 'Adapting Agriculture to Climate Change'. The project aims to protect, collect and prepare the wild relatives of 29 key food crops, including alfalfa, so that they are available to pre-breeders for the development of new varieties that are more resilient to the effects of climate change.
Millennium Seed Bank: Seed storage
The Millennium Seed Bank Partnership aims to save plants worldwide, focusing on those plants which are under threat and those which are of most use in the future. Once seeds have been collected they are dried, packaged and stored at -20°C in our seed bank vault.
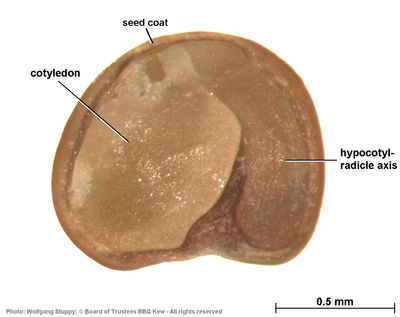
Description of seeds: Average 1,000 seed weight = 2 g
Number of seed collections stored in the Millennium Seed Bank: Three
Seed storage behaviour: Orthodox (the seeds of this plant can be dried to low moisture contents without significantly reducing their viability. This means they are suitable for long-term frozen storage such as at the MSB)
Germination testing: Successful
This species at Kew
Pressed and dried specimens of Medicago sativa are held in Kew's Herbarium, where they are available to researchers by appointment. Details and images, of some of these specimens can be seen online in Kew's Herbarium Catalogue.