Legumes of the World. Edited by G. Lewis, B. Schrire, B. MacKinder & M. Lock. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. (2005)
-
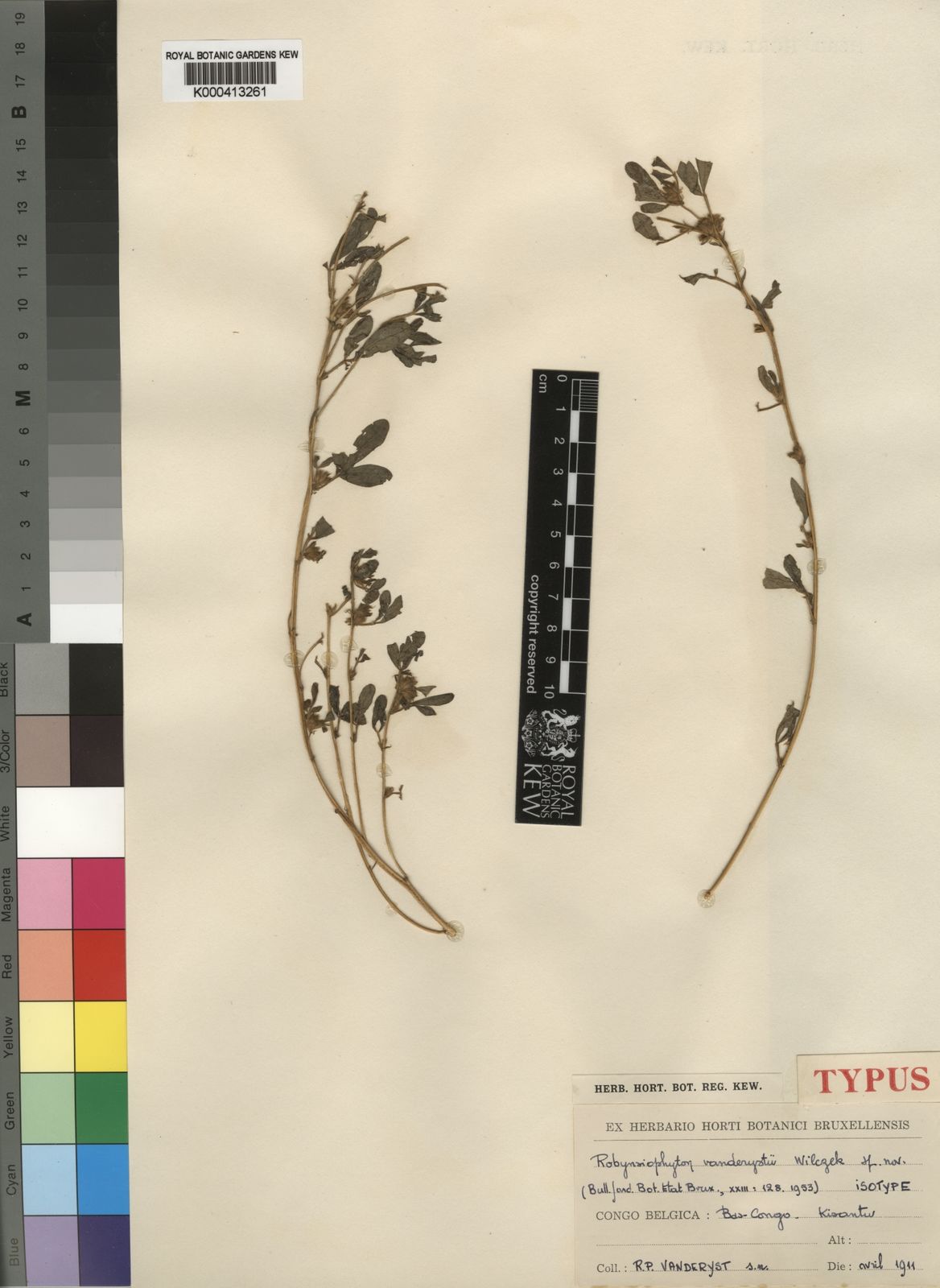
Habit
-
Herb
-
Ecology
-
Seasonally dry tropical grassland and deciduous woodland
-
Distribution
-
SC Africa (Angola, Zambia and Congo [Kinshasa])
-
Note
-
Closely related to Rothia but the flower has nine stamens of which only five are fertile
The current state of knowledge of the Crotalarieae was reviewed by Van Wyk (1991a) and by Van Wyk & Schutte (1995a). The most conspicuous recent change has been the exclusion of the Argyrolobium group (six genera, i.e. Argyrolobium, Dichilus, Melolobium, Polhillia, Anarthrophyllum and Sellocharis), which belong in tribe Genisteae rather than in Crotalarieae, where they were previously placed (Polhill, 1981q: 399 –402). New insights into relationships within the tribe have come mainly from chemosystematic studies of alkaloids (summarised in Van Wyk & Verdoorn, 1990) and several recent generic monographs (see below).
The Crotalarieae forms part of a monophyletic clade, the ‘core genistoids’ (Fig. 36) which also includes Genisteae, Podalyrieae, Thermopsideae, Brongniartieae, Euchresteae and Sophoreae sens. strict. (Crisp et al., 2000; Pennington et al., 2000a; Kajita et al., 2001). Crotalarieae appears to be sister to the Genisteae and both are sister to the Podalyrieae (Crisp et al., 2000; Wojciechowski et al., 2004). This clade is in turn sister to the Thermopsideae and Sophoreae sens. strict. (including Euchresteae).
The Crotalarieae shares with the Podalyrieae the absence of a-pyridone alkaloids such as cytisine and anagyrine that are a typical feature of all other ‘core genistoid’ tribes. Despite a lack of defining characters, the monophyly of the tribe as circumscribed here is well supported by molecular evidence (Crisp et al., 2000; Wink & Mohamed, 2003) and by cladistic analyses of morphological, cytological and chemical characters (Van Wyk & Schutte, 1995a). The latter study suggested an early diversification of the genera with uniform anthers and lupanine-type esters of quinolizidine alkaloids (Pearsonia, Rothia and Robynsiophyton) followed by the poorly known Spartidium and then the so-called ‘Cape group of genera’ (Polhill, 1981q: 399–402), which now includes Lotononis and Crotalaria. Relationships between the seven genera of the ‘Cape group’ remains unresolved despite several recent molecular studies because sampling is still relatively poor. However, a basally branching position in the tribe of the ‘Cape group’, notably Lebeckia and Wiborgia — as considered by Polhill (1976, 1981q) — is now accepted here. The exclusion of the Argyrolobium group, based on morphological and chemical characters, is also strongly supported by DNA sequence data. Due to reticulate and overlapping patterns of character state distribution in the Crotalarieae sens. strict., generic delimitations are intricate and subject to misinterpretation. Several of the large and diverse genera appear to be either monophyletic or paraphyletic depending on the choice of characters. As currently circumscribed the tribe includes 11 genera and c. 1204 species (Fig. 37).