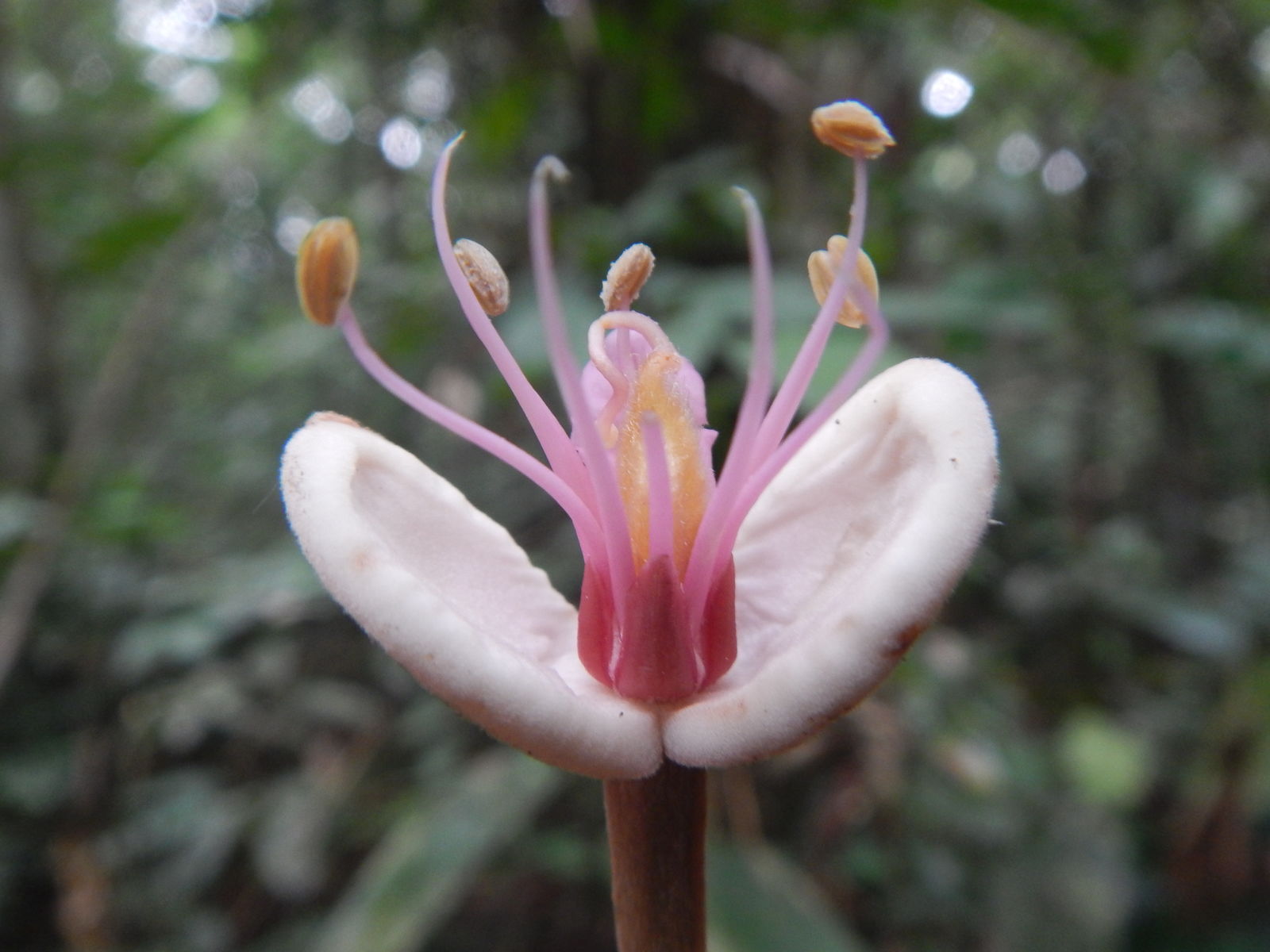
This and the following five genera form a strongly supported clade (Gervais & Bruneau, 2002; also called the 'babjit' clade sensu Wieringa & Gervais, 2003), within the exclusively African Macrolobieae clade (sensu Bruneau et al., 2001). The position of J. pellegriniana Troupin (= Paraberlinia Pellegr.) within Julbernardia is uncertain (Bruneau et al., 2001; Wieringa & Gervais, 2003), as sampling remains poor; Thylacanthus Tul., thought to be a monotypic genus from Brazil, is based on a single collection of J. paniculata (Benth.) Troupin from Mozambique (Breteler, pers. comm.)
The Detarieae sens. lat. are pantropical in distribution, with c. 58% of the genera confined to Africa (incl. Madagascar), c. 20% to the Neotropics, and c. 12% to tropical Asia. Only Copaifera, Crudia and Cynometra are pantropical (and all possibly non monophyletic) and Afzelia, Guibourtia, Hymenaea, Intsia and Sindora are native to at least two of these regions. The apparent high level of diversity in the African tropics may in part be an artefact of the (relatively) greater taxonomic effort that has been invested in the study of the African taxa. Characteristic of African Detarieae taxonomy has been the splitting off of disparate elements as segregate genera, while this has often not been the case in the Neotropics. Both regions, however, currently contain large paraphyletic assemblages requiring detailed species-level analysis. Eighty-two genera and from (729) – 747 – (765) species are treated here in Detarieae sens. lat. (Fig. 21). Of the 132 (extant) species so far assessed for IUCN red data status, 97 have categories of threat. Of these 73 are assessed as vulnerable, 13 are endangered and 11 are critically endangered.
The remarkable range and complex patterns of floral modifications found in the Detarieae sens. lat. have proved a considerable challenge to the establishment of widely accepted and clearly circumscribed generic groupings. Based on the work of Léonard (1957) and Cowan & Polhill (1981a & b), ten informal groups of genera were proposed; the Cynometra, Hymenostegia, Hymenaea, Crudia, Detarium and Brownea groups in tribe Detarieae, and the Berlinia, Macrolobium, Amherstia and Brachystegia groups in tribe Amherstieae. Genera with imbricate bracteole aestivation were assigned to Detarieae whilst those with valvate bracteole aestivation were placed in Amherstieae. Polhill (1994) retained these generic groupings with a few additions to accommodate recently described genera, and merged the two tribes into a single broadly defined tribe, Detarieae sens. lat. Breteler (1995) proposed the recognition of two tribes within Detarieae sens. lat., separated according to the relative size and position of the paired bracteoles before anthesis. Essentially, this resulted in the reassignment of Cowan & Polhill’s Amherstia group genera (Amherstia, Tamarindus and Humboldtia) from Amherstieae to Detarieae with the remaining genera forming tribe Macrolobieae. In 1999, Breteler (pers. comm.) proposed a modified Breteler (1995) tribal system in which Macrolobieae was maintained, the circumscription of Detarieae was greatly narrowed and the genera newly excluded from Detarieae were together recognised as Cynometreae sens. strict.
The first comprehensive studies of phylogenetic relationships in tribe Detarieae sens. lat., were the analyses of Bruneau et al. (2000; 2001), based on nucleotide sequence data from the chloroplast trnL intron. They found that tribes Detarieae and Macrolobieae formed a well supported monophyletic group, which included all genera placed previously in Detarieae sens. lat., except Umtiza. Bruneau et al. (2000) examined 71 genera, with the African taxa most widely sampled. The key results of the analysis were that none of the generic groupings proposed by Cowan and Polhill (1981a & b) and Polhill (1994) were supported as strictly monophyletic, and the majority of the members of tribe Macrolobieae (although not Macrolobium) were placed as a monophyletic group derived within Detarieae sens. lat. These analyses also repeatedly recognised a second group of related genera made up entirely of resin-producing taxa, with the exception of some species of Guibourtia. The resins can be seen as translucent gland dots in the leaflets and (sometimes) other organs. Within the resin producing taxa, the genus Prioria and several members of Cowan & Polhill’s Crudia group were consistently placed together (see taxonomic notes under individual genera in main text). Another subclade within the resin-producing Detarieae comprising six members of Polhill’s Detarium group was repeatedly recognised (Bruneau et al., 2000; 2001; Fougère-Danezan et al., 2003). In addition, in the trnL intron analysis, the five sampled members of Cowan and Polhill’s Brownea group were consistently placed together with Macrolobium, although this grouping was not upheld in a more recent molecular and combined molecular-morphological analysis (Herendeen et al., 2003a). Within the exclusively African Macrolobieae of Bruneau et al. (2001), a well supported subclade of six genera was recognised by Gervais & Bruneau (2002) and as the ‘babjit’ clade sensu Wieringa & Gervais (2003). Bruneau et al. (2000; 2001) confirmed the view of Polhill (1994) that the two tribes Detarieae and Macrolobieae (sensu Breteler, 1995) are best considered a single entity. Evidence from ontogenetic studies by Tucker (2000, 2001, 2002a) challenged the validity of bracteole aestivation as a criterion for subdividing Detarieae sens. lat. and identified a set of character states associated with two modes of floral development (Circular and Omega) whose distribution amongst detarioid genera does not support Polhill’s groups.
The analyses of Herendeen et al. (2003a) united a morphological dataset with the chloroplast trnL intron dataset of Bruneau et al. (2001). The combined analysis provided mixed results within Detarieae sens. lat. compared with the molecular dataset alone. Near the base of the clade, and within some subclades, greater resolution was provided but as several groups were not well supported, it would be premature to emphasise the details of this greater resolution. Elsewhere the addition of morphological characters produced weaker resolution and a less robust phylogeny due either to conflicting phylogenetic signal or increased homoplasy in the morphological data or both. The order of taxa followed here (Fig. 21) represents a synthesis of the present understanding of putative relationships within this (perhaps most morphologically diverse) tribe in the Leguminosae. Unsampled genera in the combined analysis are inserted into this order where morphological evidence appears to suggest close relationships.
Whilst significant progress has been made since Polhill (1994), further studies (particularly including the non-African members of the larger and less well understood genera) are needed before a new comprehensive classification of the Detarieae sens. lat., based on a synthesis of all available data, can be established.